In this article, we are going to understand step by step process to create Informatica Data Quality (IDQ) mapping to make external Web Service calls using Java transformation.
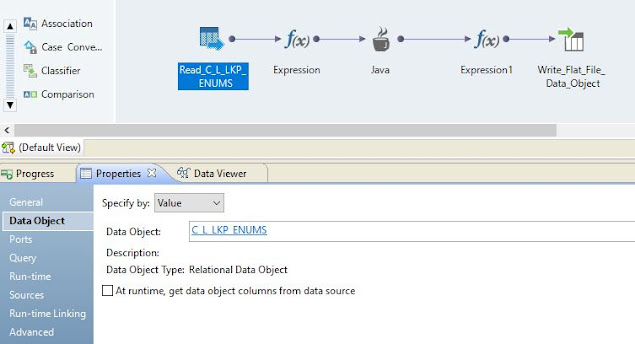
A. Overview of mapping
The mapping contains 5 major components. The first component is the source file. We can use a file or a database table as input this mapping which can hold basic information. The second component is an expression to convert input values to make them suitable for Java transformation. The third component is Java transformation which contains logic to make a call the web service. The next component is an output expression to transform the response from Java expression into output format. The last component is a target file or a database table to populate response.
The source in the mapping can be a flat file or database table. It will contain the input required for Web Service. e.g. Web Service URL, Username, Password, Context etc.
The source expression will be used to convert input values into suitable Java transformation input. e.g. Join multiple sources attributes to create URL, prepare the web service endpoint URL, populate username and password, or any other custom processing etc.
D. Java Transformation

c) Call Web Service
D. Java Transformation
The Java transformation can be used to call external or internal Web Service. In this example, we are going to call external web service.
a) Import jar file
Import all the required files and store at local system or Unix box. The IDQ mapping should read access to these files so that those can be loaded in JVM. Once all the required jars are stored, set the classpath variable under the Advanced section and point it to each of the jar files.

b) Import classes
Import all the java classes which are required to call web service. Here is screenshot with sample java classes used during the Web Service call.
Once we have all the required information to call Web Service, write a logic to handle the business requirement. In the java logic below, we are calling web service two times. From the first web service call, we are getting the response and sending that response in second web service call and then we are getting the final output.
The sample code is here,
/**
* Author : Abc
* This Java code is used to get status of the the input task and wait until it become 'SUCCESS'
*
* Input Parameters:
* taskName - Input taskflow
* urlSubmit - Web service endpoint to get RunId for input taskflow
* urlGetStatus - Web service endpoint to get status using RunId
* loginUid - Userid for authentication
* loginPwd - Password for authentication
*/
try {
// Step 1: Get RunId using Web Service endpoint and task name
String url = "https://localhost:8080/TaskName";
// String url = urlSubmit + taskName;
String name = "abcuser";
// String name = loginUid;
String password = "abcpassword;
// String password = loginPwd;
String authString = name + ":" + password;
String authStringEnc = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(authString.getBytes());
Client restClient = Client.create();
WebResource webResource = restClient.resource(url);
ClientResponse resp = webResource.accept("application/json").header("Authorization", "Basic " + authStringEnc).get(ClientResponse.class);
String stTaskIdMessage = resp.getEntity(String.class);
// Step 2: Parse response to get RunId from Web Service for given task
JSONParser jsonParser = new JSONParser();
JSONObject jsonObj = (JSONObject) jsonParser.parse(stTaskIdMessage);
String stRunId = (String) jsonObj.get("RunId");
// Step 3: Call Web service endpoint to get status of input taskflow and check if it not in 'RUNNING' state.
// If it is in RUNNING stage, wait until the state changes.
boolean isRunning = true;
String stStatus = "";
while (isRunning) {
String url2 = "https://localhost:8080/task/status/"+stRunId;
WebResource webResourceStatus = restClient.resource(url2);
ClientResponse respStatus = webResourceStatus.accept("application/json").header("Authorization", "Basic " + authStringEnc).get(ClientResponse.class);
String stStatusMessage = respStatus.getEntity(String.class);
JSONObject jsonStatusObj = (JSONObject) jsonParser.parse(stStatusMessage);
stStatus = (String) jsonStatusObj.get("status");
if (!stStatus.contentEquals("RUNNING") ) {
isRunning = false;
} else {
Thread.sleep(10000); // Value is in millisecond. Currently it is set for 10 seconds
}
}
runId = stRunId;
status = stStatus; // Return status to output field.
}
catch (Exception e) { // Required to handle exception which is thrown from JSON Parser.
e.printStackTrace();
}
* Author : Abc
* This Java code is used to get status of the the input task and wait until it become 'SUCCESS'
*
* Input Parameters:
* taskName - Input taskflow
* urlSubmit - Web service endpoint to get RunId for input taskflow
* urlGetStatus - Web service endpoint to get status using RunId
* loginUid - Userid for authentication
* loginPwd - Password for authentication
*/
try {
// Step 1: Get RunId using Web Service endpoint and task name
String url = "https://localhost:8080/TaskName";
// String url = urlSubmit + taskName;
String name = "abcuser";
// String name = loginUid;
String password = "abcpassword;
// String password = loginPwd;
String authString = name + ":" + password;
String authStringEnc = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(authString.getBytes());
Client restClient = Client.create();
WebResource webResource = restClient.resource(url);
ClientResponse resp = webResource.accept("application/json").header("Authorization", "Basic " + authStringEnc).get(ClientResponse.class);
String stTaskIdMessage = resp.getEntity(String.class);
// Step 2: Parse response to get RunId from Web Service for given task
JSONParser jsonParser = new JSONParser();
JSONObject jsonObj = (JSONObject) jsonParser.parse(stTaskIdMessage);
String stRunId = (String) jsonObj.get("RunId");
// Step 3: Call Web service endpoint to get status of input taskflow and check if it not in 'RUNNING' state.
// If it is in RUNNING stage, wait until the state changes.
boolean isRunning = true;
String stStatus = "";
while (isRunning) {
String url2 = "https://localhost:8080/task/status/"+stRunId;
WebResource webResourceStatus = restClient.resource(url2);
ClientResponse respStatus = webResourceStatus.accept("application/json").header("Authorization", "Basic " + authStringEnc).get(ClientResponse.class);
String stStatusMessage = respStatus.getEntity(String.class);
JSONObject jsonStatusObj = (JSONObject) jsonParser.parse(stStatusMessage);
stStatus = (String) jsonStatusObj.get("status");
if (!stStatus.contentEquals("RUNNING") ) {
isRunning = false;
} else {
Thread.sleep(10000); // Value is in millisecond. Currently it is set for 10 seconds
}
}
runId = stRunId;
status = stStatus; // Return status to output field.
}
catch (Exception e) { // Required to handle exception which is thrown from JSON Parser.
e.printStackTrace();
}
d) Call Web Service
The full source code can be accessed from Java -> Full code. This will give broader view of how the Java code executed at run time.
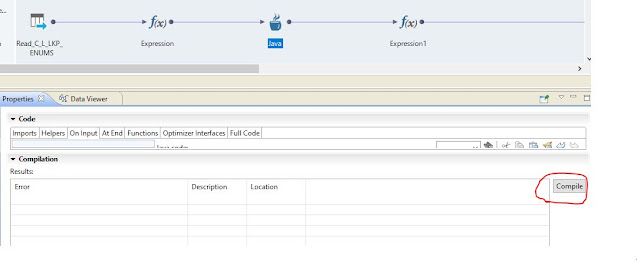
e) Compile code
Once the code completed then compile to code in order to generate .class files load in the memory. In order to compile the code user section - Advanced -> Properties -> Compilation
E. Output Expression
Create output expression to translate the output from Java transformation into the output file or database table.
Create output file or database table in order to populate the final response output. The output can be used for business use purposes.








No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.